Sveltos Templating: Cilium Cluster Mesh in One Run
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how to dynamically instantiate Kubernetes resources before deploying them to a cluster? What if I tell you there is an easy way to do it? Sveltos lets you define add-ons and applications using templates. Before deploying any resource down the managed clusters, Sveltos instantiates the templates using information gathered from the management cluster.
In a previous post, we outlined a step-by-step approach to forming a Cilium cluster mesh between two clusters. In today's post, we will demonstrate how the Sveltos templating is used to deploy a Cilium cluster mesh dynamically in one go.
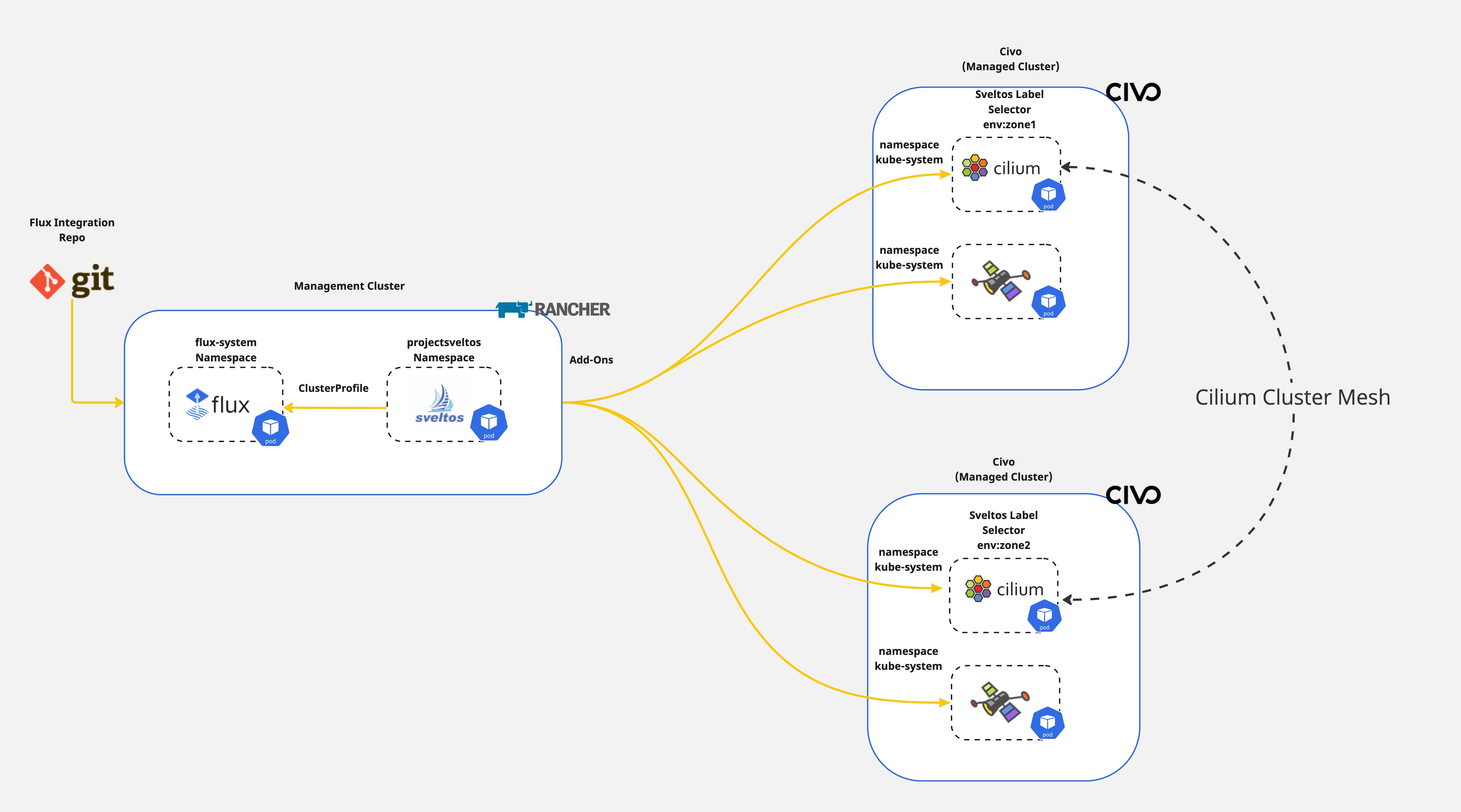
Lab Setup
+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------+
| Cluster Name | Type | Version |
+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------+
| mgmt | Mgmt Cluster | v1.28.9+rke2r1 |
| mesh01 | Managed Cluster | v1.29.2+k3s1 |
| mesh02 | Managed Cluster | v1.29.2+k3s1 |
+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------+
+-------------+----------+
| Deployment | Version |
+-------------+----------+
| Cilium | v1.15.6 |
| sveltosctl | v0.32.0 |
+-------------+----------+
Prerequisites
To follow along, ensure the below are satisfied.
- A management cluster with Sveltos installed
- kubectl installed
- sveltosctl installed
If you are unaware of how to install Sveltos in a Kubernetes cluster, follow the instructions mentioned here.
Step 1: Register Clusters with Sveltos
For this demonstration the Civo Kubernetes cluster offering was used. Once the clusters are ready, it is time to proceed with the Sveltos cluster registration. To do that, we will utilise sveltosctl and generate a new kubeconfig file.
$ sveltosctl register cluster --namespace=<namespace> --cluster=<cluster name> \
--kubeconfig=<path to Sveltos file with Kubeconfig> \
--labels=key=value
Example - mesh01 registration
$ sveltosctl register cluster --namespace=civo --cluster=mesh01 \
--kubeconfig=/home/test/mesh01.yaml \
--labels=cilium=zone01
We will register the clusters with Sveltos on the mentioned namespace, name, and will attach the cluster labels cilium=zone01 and cilium=zone02 respectively.
If the namespace does not exist in the management cluster, the command will fail with the namespace not found error. Ensure the defined namespace exists in the cluster before registration.
Validation
$ export KUBECONFIG=<Sveltos managament cluster>
$ kubectl get sveltoscluster -A --show-labels
NAMESPACE NAME READY VERSION LABELS
civo mesh01 true v1.29.2+k3s1 cilium=zone01
civo mesh02 true v1.29.2+k3s1 cilium=zone02
mgmt mgmt true v1.28.9+rke2r1 sveltos-agent=present
Step 2: Deploy Cilium Cluster Mesh ConfigMap
Before we even start working with the Sveltos templating, we will deploy two ConfigMap resources that include the Cilium Cluster Mesh configuration.
Example - mesh01 ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cilium-config-mesh01
namespace: civo
data:
id: "1"
k8sServiceHost: "74.220.x.x"
k8sServicePort: "6443"
nodePort: "32379"
crt: "Define the base64 ca.crt"
key: "Define the base64 ca.key"
clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList: "10.244.0.0/16"
peermeshname: "mesh02"
peermeship: "192.168.x.x"
peermeshport: "32380"
From the YAML definition, it is clear the resources we would like to deploy are in a key-value format. The ConfigMap for both clusters contains the required information to form a Cilium cluster mesh seamlessly.
Deploy ConfigMap Management Cluster
$ export KUBECONFIG=<Sveltos managament cluster>
$ kubectl apply -f config_mesh01.yaml,config_mesh02.yaml
$ kubectl get cm -n civo
NAME DATA AGE
cilium-config-mesh01 10 9s
cilium-config-mesh02 10 5s
kube-root-ca.crt 1 23m
As the Kubernetes managed clusters are registered in the civo namespace, the ConfigMaps are defined there.
Step 3: Deploy Sveltos ClusterProfile
We will create a Sveltos ClusterProfile to install Cilium as a CNI alongside the Hubble UI and Cilium cluster mesh by instantiating the configuration from the information located in the ConfigMap created in previous step.
Example - mesh01 ClusterProfile
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: cilium-1156-zone01
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
cilium: zone01
templateResourceRefs:
- resource:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
name: cilium-config-{{ .Cluster.metadata.name }}
identifier: CiliumConfig
helmCharts:
- chartName: cilium/cilium
chartVersion: 1.15.6
helmChartAction: Install
releaseName: cilium
releaseNamespace: kube-system
repositoryName: cilium
repositoryURL: https://helm.cilium.io/
values: |
tls:
ca:
cert: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.crt }}
key: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.key }}
cluster:
id: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.id }}
name: {{ .Cluster.metadata.name }}
clustermesh:
apiserver:
replicas: 2
service:
type: NodePort
nodePort: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.nodePort }}
tls:
authMode: cluster
server:
extraDnsNames:
- "{{ .Cluster.metadata.name }}.mesh.cilium.io"
config:
clusters:
- address: ""
ips:
- {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.peermeship }} # The Node IP of the available nodes or a resolvable hostname
name: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.peermeshname }}
port: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.peermeshport }}
enabled: true
domain: "mesh.cilium.io"
useAPIServer: true # This is required for the Cluster Mesh setup
kubeProxyReplacement: true
k8sServiceHost: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.k8sServiceHost }}
k8sServicePort: {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.k8sServicePort }}
hubble:
enabled: true
peerService:
clusterDomain: cluster.local
relay:
enabled: true
tls:
auto:
certValidityDuration: 1095
enabled: true
method: helm
ui:
enabled: true
nodeinit:
enabled: true
ipam:
mode: cluster-pool
operator:
clusterPoolIPv4MaskSize: "24"
clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList:
- {{ (getResource "CiliumConfig").data.clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList }}
nodePort:
enabled: true
debug:
enabled: true
The ClusterProfile will get deployed to the managed clusters with the label set to cilium:zone01. Once a cluster is found, we instruct Sveltos to use the templateResourceRefs capability and use the details found in the ConfgiMap with the name set to cilium-config-{{ .Cluster.metadata.name }}. This will match the cilium-config-mesh01 and cilium-config-mesh02 ConfigMap. Then, we instruct Sveltos to install the Cilium Helm chart v1.15.6.
For the Cilium Helm chart instantiation, we go through the ConfigMap and populate the values based on the key definition.
We deploy a Cilium cluster mesh with a common TLS certificate and a NodePort service. For the production environment, it is recommended to deploy a LoadBalancer setup. The above template can be used by updating the clustermesh.service.type=LoadBalancer and setting the standard service Port.
Deploy ClusterProfile Management Cluster
$ export KUBECONFIG=<Sveltos managament cluster>
$ kubectl apply -f clusterprofile_mesh01.yaml,clusterprofile_mesh02.yaml
Step 4: Validate Results
Validation - sveltosctl
$ ./sveltosctl show addons
+-------------+---------------+-------------+--------+---------+--------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
| CLUSTER | RESOURCE TYPE | NAMESPACE | NAME | VERSION | TIME | PROFILES |
+-------------+---------------+-------------+--------+---------+--------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
| civo/mesh01 | helm chart | kube-system | cilium | 1.15.6 | 2024-08-10 22:38:33 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/cilium-1156-zone01 |
| civo/mesh02 | helm chart | kube-system | cilium | 1.15.6 | 2024-08-10 22:38:55 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/cilium-1156-zone02 |
+-------------+---------------+-------------+--------+---------+--------------------------------+-----------------------------------+
Validation - mesh01
$ kubectl exec -it -n kube-system cilium-888jc -c cilium-agent -- cilium-dbg troubleshoot clustermesh mesh02
Found 1 remote cluster configurations
Troubleshooting filtered subset of clusters: mesh02
Remote cluster "mesh02":
📄 Configuration path: /var/lib/cilium/clustermesh/mesh02
🔌 Endpoints:
- https://mesh02.mesh.cilium.io:32380
✅ Hostname resolved to: 192.168.x.x
✅ TCP connection successfully established to 192.168.x.x:32380
✅ TLS connection successfully established to 192.168.x.x:32380
ℹ️ Negotiated TLS version: TLS 1.3, ciphersuite TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
ℹ️ Etcd server version: 3.5.14
🔑 Digital certificates:
✅ TLS Root CA certificates:
- Serial number: 2c:b4:43:9c:fb:82:62:4f:55:0f:eb:5e:a4:fe:af:5e:14:95:18:74
Subject: CN=Cilium LAB CA
Issuer: CN=Cilium LAB CA
Validity:
Not before: 2024-04-25 14:04:31 +0000 UTC
Not after: 2034-04-23 14:04:31 +0000 UTC
✅ TLS client certificates:
- Serial number: 13:8f:38:4e:e9:08:bb:81:93:20:ff:30:33:ed:fb:13
Subject: CN=remote-mesh01
Issuer: CN=Cilium LAB CA
Validity:
Not before: 2024-08-10 20:53:31 +0000 UTC
Not after: 2027-08-10 20:53:31 +0000 UTC
⚙️ Etcd client:
✅ Etcd connection successfully established
ℹ️ Etcd cluster ID: 820847063f6cabce
Validation - mesh02
$ kubectl exec -it -n kube-system cilium-94ddz -c cilium-agent -- cilium-dbg troubleshoot clustermesh mesh01
Found 1 remote cluster configurations
Troubleshooting filtered subset of clusters: mesh01
Remote cluster "mesh01":
📄 Configuration path: /var/lib/cilium/clustermesh/mesh01
🔌 Endpoints:
- https://mesh01.mesh.cilium.io:32379
✅ Hostname resolved to: 192.168.x.x
✅ TCP connection successfully established to 192.168.x.x:32379
✅ TLS connection successfully established to 192.168.x.x:32379
ℹ️ Negotiated TLS version: TLS 1.3, ciphersuite TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
ℹ️ Etcd server version: 3.5.14
🔑 Digital certificates:
✅ TLS Root CA certificates:
- Serial number: 2c:b4:43:9c:fb:82:62:4f:55:0f:eb:5e:a4:fe:af:5e:14:95:18:74
Subject: CN=Cilium LAB CA
Issuer: CN=Cilium LAB CA
Validity:
Not before: 2024-04-25 14:04:31 +0000 UTC
Not after: 2034-04-23 14:04:31 +0000 UTC
✅ TLS client certificates:
- Serial number: 94:02:e1:4a:b8:74:4c:d7:62:af:c1:d8:19:a8:3b:8f
Subject: CN=remote-mesh02
Issuer: CN=Cilium LAB CA
Validity:
Not before: 2024-08-10 20:59:07 +0000 UTC
Not after: 2027-08-10 20:59:07 +0000 UTC
⚙️ Etcd client:
✅ Etcd connection successfully established
ℹ️ Etcd cluster ID: 21f7360bef94b707
Cilium cluster mesh is deployed in one run without the need for an additional Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool or additional rendering!
![]()
Sveltos Templating Benefits
Sveltos templating enables users to utilise the same add-on configuration across different clusters while allowing variations like different add-on configuration values.
Sveltos lets users define add-ons and applications in a reusable way. We can deploy the definitions across multiple clusters with minor adjustments. The approach saves time, effort, and headaches, especially in large-scale environments.
Conclusions
In a couple of minutes and with a minimal configuration effort we formed a cluster mesh between two Kubernetes clusters. This is the power of Sveltos templating.
If you want to explore a step-by-step guide on how to setup a Cilium cluster mesh, have a look at my previous blog post here.
✉️ Contact
We are here to help! Whether you have questions, or issues or need assistance, our Slack channel is the perfect place for you. Click here to join us us.
👏 Support this project
Every contribution counts! If you enjoyed this article, check out the Projectsveltos GitHub repo. You can star 🌟 the project if you find it helpful.
The GitHub repo is a great resource for getting started with the project. It contains the code, documentation, and many more examples.
Thanks for reading!
