Sveltos: Optimising Day-2 Operations with Cilium and Tetragon
Introduction
How easy is it to handle Day-2 operations with existing CI/CD tooling? Sveltos provides the ability to perform not only Day-1 operations but also helps platform administrators, tenant administrators and other operators with Day-2 operations. For example, we can use the HealthCheck and the ClusterHealthCheck features to not only watch the health of a cluster but also collect information from the managed clusters and display them in the management cluster.
In today's blog post, we will cover a way of deploying Cilium as our CNI alongside Cilium Tetragon for observability. We will then continue with a simple TracingPolicy deployment to capture socket connections and then use Sveltos to display the tracing results back to the management cluster.
The goal of the demonstration is to showcase how Sveltos can be used for different Kubernetes cluster operations based on the use case at hand.
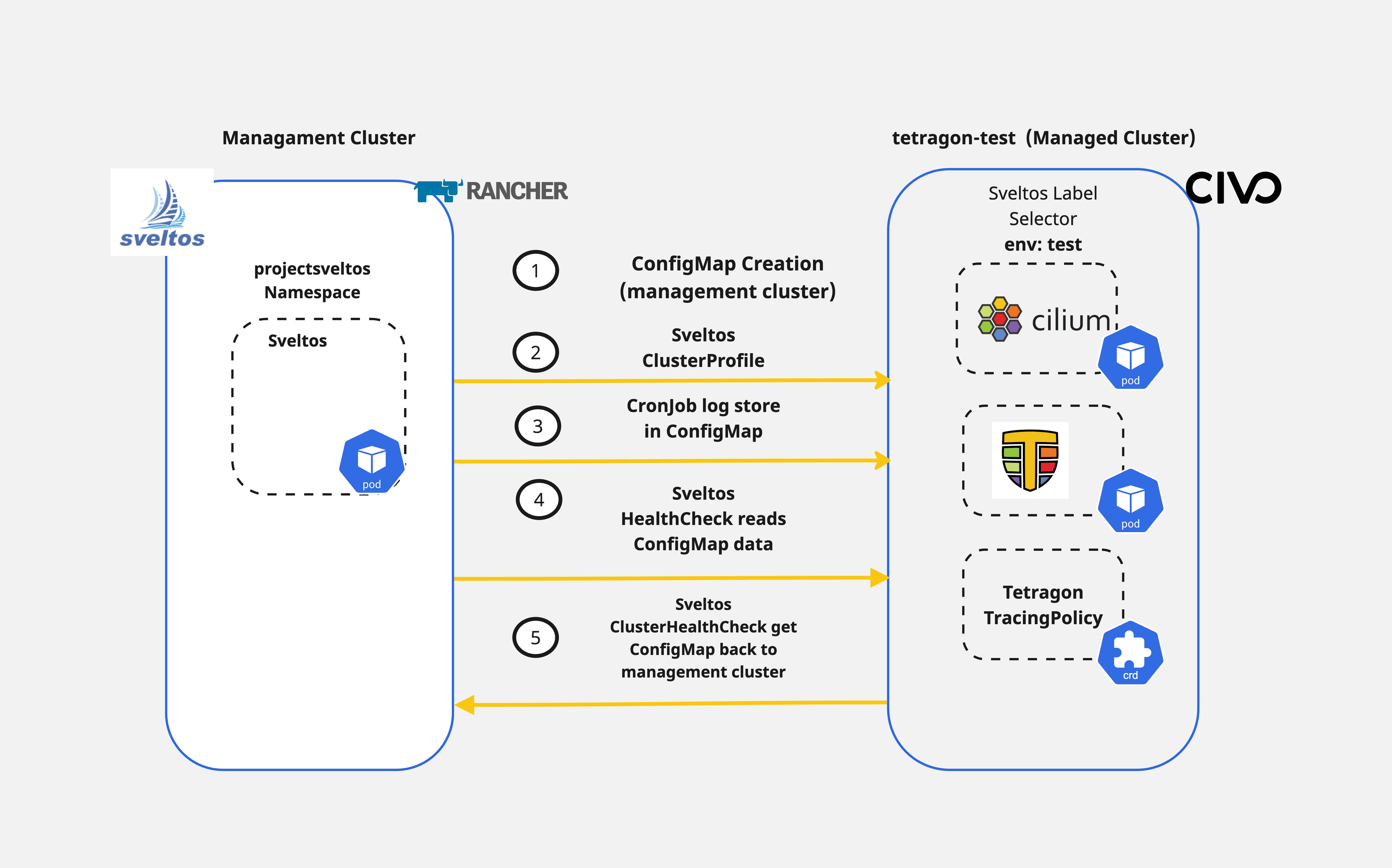
Lab Setup
+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------+
| Cluster Name | Type | Version |
+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------+
| mgmt | Mgmt Cluster | v1.28.9+rke2r1 |
| tetragon-test | Managed Cluster | v1.29.2+k3s1 |
+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------+
+-------------+---------------------+
| Deployment | Version |
+-------------+---------------------+
| Cilium | v1.16.1 |
| Tetragon | v1.2.0 |
| sveltosctl | v0.37.0 |
+-------------+---------------------+
GitHub Resources
The YAML definition files are located here.
Prerequisites
To follow along, ensure the below are satisfied.
- A management cluster with Sveltos installed
- kubectl installed
- sveltosctl installed
If you are unaware of installing Sveltos in a Kubernetes cluster, follow the instructions mentioned here.
Step 1: Cluster Registration with Sveltos
Once the Kubernetes cluster is ready, we can continue with the Sveltos registration. To do that, we will utilise sveltosctl. The sveltosctl can be downloaded here.
Example Registration
$ sveltosctl register cluster --namespace=test --cluster=tetragon-test \
--kubeconfig=/home/test/tetragon-test.yaml \
--labels=env=test
The cluster above will be registered with Sveltos on the mentioned namespace, and name, and will attach the cluster labels to perform different deployment versions.
If the namespace does not exist in the management cluster, the command will fail with the namespace not found error. Ensure the defined namespace exists in the cluster before registration.
Validation
$ export KUBECONFIG=<Sveltos managament cluster>
$ kubectl get sveltoscluster -A --show-labels
NAMESPACE NAME READY VERSION LABELS
mgmt mgmt true v1.28.9+rke2r1 projectsveltos.io/k8s-version=v1.28.9,sveltos-agent=present
test tetragon-test true v1.29.2+k3s1 env=test,projectsveltos.io/k8s-version=v1.29.2,sveltos-agent=present
Ensure the labels set are correct. We will use them at a later step.
Step 2: Custom ConfigMap, Cilium, Tetragon Deployment
As a first step, we will deploy Cilium and Cilium Tetragon to the clusters with the label set to env:test. Then, we will deploy a ConfigMap on the management cluster and allow Sveltos to deploy a TracingPolicy alongside a CronJob that polls tracing events every 2 minutes from the targeted managed cluster.
ClusterProfile - Cilium, Tetragon, and ConfigMap
---
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: tetragon-test-deploy
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: test
helmCharts:
- chartName: cilium/cilium
chartVersion: 1.16.1
helmChartAction: Install
releaseName: cilium
releaseNamespace: kube-system
repositoryName: cilium
repositoryURL: https://helm.cilium.io/
- chartName: cilium/tetragon
chartVersion: 1.2.0
helmChartAction: Install
releaseName: tetragon
releaseNamespace: kube-system
repositoryName: tetragon
repositoryURL: https://helm.cilium.io/
policyRefs:
- name: tetragon-policy-socket-log
namespace: default
kind: ConfigMap
Sveltos follows the top-down approach when it comes to add-on and application deployment. First, Cilium will get deployed as our CNI. Next, then Tetragon and afterwards, we proceed with the deployment of a ConfigMap with the name tetragon-policy-socket-log which has already been deployed in the management cluster.
A copy of the ConfigMap YAML definition is located here.
Deploy ConfigMap and ClusterProfile - Management Cluster
$ export KUBECONFIG=<Sveltos managament cluster>
$ kubectl apply -f tetragon_cm.yaml,clusterprofile_tetragon.yaml
Validation - Management Cluster
$ ./sveltosctl show addons
+--------------------+----------------------------------------------+-------------+-------------------------------+---------+--------------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| CLUSTER | RESOURCE TYPE | NAMESPACE | NAME | VERSION | TIME | PROFILES |
+--------------------+----------------------------------------------+-------------+-------------------------------+---------+--------------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| test/tetragon-test | helm chart | kube-system | cilium | 1.16.1 | 2024-10-06 09:28:12 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
| test/tetragon-test | helm chart | kube-system | tetragon | 1.2.0 | 2024-10-06 09:28:15 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
| test/tetragon-test | rbac.authorization.k8s.io:ClusterRoleBinding | | tetragon-cluster-role-binding | N/A | 2024-10-06 09:28:12 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
| test/tetragon-test | batch:CronJob | default | tetragon-log-fetcher | N/A | 2024-10-06 09:28:12 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
| test/tetragon-test | cilium.io:TracingPolicy | | networking | N/A | 2024-10-06 09:28:12 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
| test/tetragon-test | :ServiceAccount | default | tetragon-sa | N/A | 2024-10-06 09:28:12 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
| test/tetragon-test | rbac.authorization.k8s.io:ClusterRole | | tetragon-cluster-role | N/A | 2024-10-06 09:28:12 +0200 CEST | ClusterProfile/tetragon-test-deploy |
+--------------------+----------------------------------------------+-------------+-------------------------------+---------+--------------------------------+-------------------------------------+
Validation - Managed Cluster
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep -E "cilium|tetragon"
cilium-operator-8547744bd7-qhl7r 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
cilium-operator-8547744bd7-m26lh 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
tetragon-mln8g 2/2 Running 0 4m29s
tetragon-c7gwj 2/2 Running 0 4m29s
tetragon-tjx54 2/2 Running 0 4m29s
cilium-g7ftd 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
cilium-pv9gj 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
cilium-9cr4l 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
cilium-envoy-9kjnv 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
cilium-envoy-fpqkl 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
cilium-envoy-25gvv 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
tetragon-operator-55c555fcf4-s5mvs 1/1 Running 0 4m29s
$ kubectl get cronjobs,jobs,pods
NAME SCHEDULE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
cronjob.batch/tetragon-log-fetcher */2 * * * * False 0 98s 5m26s
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
job.batch/install-traefik2-nodeport-te 1/1 11s 47h
job.batch/tetragon-log-fetcher-28803330 1/1 10s 3m38s
job.batch/tetragon-log-fetcher-28803332 1/1 9s 98s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/install-traefik2-nodeport-te-zrh57 0/1 Completed 0 47h
pod/tetragon-log-fetcher-28803330-wpl9r 0/1 Completed 0 3m38s
pod/tetragon-log-fetcher-28803332-r7q5v 0/1 Completed 0 98s
Based on the output above, we have deployed Cilium, Tetragon and a CronJob to collect Tetragon logs based on a tracing policy every 2 minutes with a timeout of 5 sec. 🎉 We can proceed further and use the Sveltos ClucterHealthCheck and HealthCheck to collect the data of the newly created ConfiMap in the managed cluster.
If the defined ConfigMap or CronJob does not fit your needs, feel free to update the YAML definitions based on your liking.
Step 3: Deploy ClusterHealthCheck and HealthCheck
To be able to collect resources from the Sveltos managed cluster, we will use a new YAML definition to collect the data from the ConfigMap with the name tetragon-logs.
The ConfigMap tetragon-logs is created and patched with a periodic execution of Jobs mentioned in Step 2.
HealthCheck and ClusterHealthCheck Defintion
# Collect the resource of the ConfigMap with the name `tetragon-logs`
---
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: HealthCheck
metadata:
name: tetragon-log-fetcher
spec:
collectResources: true
resourceSelectors:
- group: ""
version: "v1"
kind: "ConfigMap"
name: tetragon-logs
namespace: default
evaluateHealth: |
function evaluate()
local statuses = {}
for _,resource in ipairs(resources) do
status = "Degraded"
table.insert(statuses, {resource=resource, status = status, message = resource.data["tetragon-logs.txt"]})
end
local hs = {}
if #statuses > 0 then
hs.resources = statuses
end
return hs
end
# Get the ConfigMap data and send it to the management cluster
---
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterHealthCheck
metadata:
name: tetragon-log-fetcher
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: test
livenessChecks:
- name: tetragon-log-fetcher
type: HealthCheck
livenessSourceRef:
kind: HealthCheck
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
name: tetragon-log-fetcher
notifications:
- name: event
type: KubernetesEvent
Deploy HealthCheck and ClusterHealthCheck - Management Cluster
$ export KUBECONFIG=<Sveltos managament cluster>
$ kubectl apply -f tetragon_healthcheck_logs.yaml
Validation - Management Cluster
$ ./sveltosctl show resources
+--------------------+---------------------+-----------+---------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| CLUSTER | GVK | NAMESPACE | NAME | MESSAGE |
+--------------------+---------------------+-----------+---------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| test/tetragon-test | /v1, Kind=ConfigMap | default | tetragon-logs | 🔌 connect kube-system/coredns-6799fbcd5-4bv5r /coredns tcp 127.0.0.1:35846 -> |
| | | | | 127.0.0.1:8080 🧹 close kube-system/coredns-6799fbcd5-4bv5r /coredns tcp 127.0.0.1:35846 |
| | | | | -> 127.0.0.1:8080 🧹 close kube-system/coredns-6799fbcd5-4bv5r /coredns tcp 127.0.0.1:8080 |
| | | | | -> 127.0.0.1:35846 🔌 connect kube-system/coredns-6799fbcd5-4bv5r /coredns tcp |
| | | | | 127.0.0.1:35852 -> 127.0.0.1:8080 🧹 close kube-system/coredns-6799fbcd5-4bv5r /coredns tcp |
| | | | | 127.0.0.1:35852 -> 127.0.0.1:8080 🧹 close kube-system/coredns-6799fbcd5-4bv5r /coredns tcp |
| | | | | 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 127.0.0.1:35852 🔌 connect k3s-tetragon-9ab2-92fa7d-node-pool-df07-7inhp |
| | | | | /var/lib/rancher/k3s/data/7d0aa19ffc230d4322f04d1ae8783e54ce189dfc4cbfa0a6afcdcabec2346d0c/bin/k3s |
+--------------------+---------------------+-----------+---------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
From the output above, we see the logs collected from the Tetragon TracingPolicy coming from a managed cluster and making them available in a management cluster! Cool, right? The same approach can be used with different data located in the managed clusters. A post written by Gianluca outlining the collection of kube-bench scanning results can be found here.
Sveltos for Day-2 Operations Benefits
Sveltos allows users to deploy the required add-on and deployments to a fleet of clusters while allowing platform administrators and operators to enhance the security posture and observability of the clusters in a simple and meaningful way. Use the Sveltos Event Framework, Tiers, ClusterHealthCheck, and HealthCheck features to enhance the posture of different platforms!
Conclusions
In a few minutes ⏳, with minimal configuration effort and following the GitOps approach, we deployed Cilium as our CNI, Cilium Tetragon for observability alongside polling and displaying of critical tracing results to the management cluster painlessly! 🎉
In the next blog posts, we will touch on topics around Day-2 operations.
Resources
- Cilium Labs: https://isovalent.com/resource-library/labs/
- Tetragon - Getting Started Lab: https://isovalent.com/labs/tetragon-getting-started/
- Sveltos ClusterHealthCheck/HealthCheck: https://projectsveltos.github.io/sveltos/observability/notifications/#example-configmap-healthcheck
- Sveltos Event Framework: https://projectsveltos.github.io/sveltos/events/addon_event_deployment/
- Sveltos Tiers: https://projectsveltos.github.io/sveltos/deployment_order/tiers/
✉️ Contact
We are here to help! Whether you have questions, or issues or need assistance, our Slack channel is the perfect place for you. Click here to join us us.
👏 Support this project
Every contribution counts! If you enjoyed this article, check out the Projectsveltos GitHub repo. You can star 🌟 the project if you find it helpful.
The GitHub repo is a great resource for getting started with the project. It contains the code, documentation, and many more examples.
Thanks for reading!
